1. Purpose.
The aim of this paper is to inspect the persistence of shamanic elements and their techniques within Western culture through the use of psychopharmacological substances, ritualistic practices, and cognitive training, which are commonly used to induce an Altered State of Consciousness (ASC) in coaction towards attaining a Sacred Ecstatic Experience (SEE) in contemporary society. That they have remained within contemporary society is adherent to their importance within the development of individual and social life. Shamanic elements of healing and their therapeutic applications will be examined in regards to how their traditional uses have been maintained, developed, and incorporated into new aspects of medical and therapeutic culture. This maintained and modified nature of shamanic elements will also be discussed on the topic of magic and intellectual property rights.
2. Importance.
Shamanism is often examined using cultural ecological terms when trying to define its presence as a religious technique within past and present cultures. A problem with this is that there have been few comprehensive assessments of the subjective effects of shamanic-like journeying techniques on non-shamans, regardless of the deviations that occur from the traditional forms to modified (self-)Treatments (Rock et al. 2008). Hayden (2003) is one of the few texts providing a comprehensive assessment of shamanic-like elements and techniques, which is termed by Hayden (2003:63) as Sacred Ecstatic Experiences (SEEs): sacred ecstatic states seem to be particularly strong experiences that can occur when a person enters into an altered state of consciousness with cultural values that predispose the person toward sacred ecstatic experiences, when individuals are motivated to have such experiences and have made appropriate ritual, mental, and physical preparations for them. The SEE is the foundation for the continuation of shamanic elements and their techniques today.

It is difficult to construct exactly all the proper terminology and criteria which must be used when building an operationally defined list of all the elements of shamans and their techniques to discuss here. This topic of operational definitions of SEE has been tackled in such a multidisciplinary way that the terminology appears diluted and confused to me (Rock et al. 2008, Dobkin de Rios 1977, Hayden 2003, Móró 2010, Suchman 1989). An objective of this paper is to briefly examine only those elements and techniques that are supported with the physical and measureable properties above the debate over the validity of subjective experience within scientific models and theories. For several decades this has been dealt within psychological research development of ASC studies and the noteworthy measure Phenomenology of Consciousness Inventory (PCI; Pekala et al. 1991).
The future also holds promise for SEEs to be researched across disciplines using a wide range of scientific approaches. As with all things in life, a hierarchy of categorization occurs. Shamanic elements and their techniques are influencing research into the neurological basis and cognitive implications of ASC upon our health, life, and the role of set and setting within therapeutic models of clinical care. Even complex legal realms of litigation of copyright laws and intellectual property rights can utilize the sacred knowledge that shamans have been using since the prehistory of religion. Absorbing for generations and apply it towards increasing and enhancing their own current perspectives.

Perspectives are what make reality. We all have our own one. Every individual has a personal sense of reality and has such themes have been perplexing philosophers for millennia and been argued on paper since the inception of academic institutions. Shamanic elements are rooted in the ability of controlling perspective, perception, sacred forces, the Force, nature, God, karma, and spirits. All of these terms exist interconnected and separated by our reality tunnels. But for the purpose of this discourse I shall use many of the above to be the same abstract concept of what it is that shamans interact with spiritually and physically.
The shaman's voluntary ability to overcome, control, and regulate the severe conditions through the invocation of SEEs places him or her in a special position when used to enhance appropriate behaviors and ameliorate stress and illness within a community (Hayden 2003:49 Krippner 1991). This is because the shaman has tapped into certain abilities to communicate with the sacred forces and reach into others reality tunnels and break free their physical illusionary shells to expose what the individual’s sacred realities could be. This is achieved through many shamanic elements and techniques; a more visible one being costumes. Costumes worn during shamanic rituals have been ethnographically shown to assist, protect and help control the connection between the shaman and the sacred forces that they invoke, also by utilizing archetypal symbolic items, enhancement of the mental states, self-confidence, and energy levels within the shaman balance of control (Hayden 2003).

To properly use a costume one needs to know how to acquire it, put it on, and invoke the associated symbolic content behind it. All of this knowledge is part of the training of the shaman and is a very crucial stage of shamanic practices. No person instantly gains insight into their own and other’s perspectives. With dedication of the individual and the help from elders, texts, experience, and practice the shaman can prepare themselves ritually and mentally for the shamanic practice ahead. Through training, individuals create automatic physical, cognitive, and behavioral reflexes, reactions, and associations in order to gain mastery over their internal mental states during ASCs and SEEs and return to their present perspective (Hayden 2003, Winkelman 1991, Krippner 1991). Neurologically this has been shown that during hallucinogen induced ASCs there is an increase of coherence in metacognitive processes and the modified oscillatory rate improves the connection of thoughts and feelings primarily to a greater degree of balance and integration of the left and right hemispheres leading to insight and a trance-like or possessive state (Winkleman 1991).

Trance and possession states though are only two type of ASC. Shamanic techniques of inducing an ASC are as varied as their symbolical worldviews and beliefs. Formal techniques that are associated with shamanism are sensory deprivation and overstimulation, pain through tattoos, initiation rites, body modification, psychoactive plants, psychopharmacological substances, and cognitive training (Hayden 2003, Winkelman 1991, Schmid et al. 2010, Rock et al. 2008). These techniques and ASC will be revisited in more detail soon.
Training teaches the shaman how those insights can be used personally and for the community. This social application of knowledge is another important element of shamanism. Not facing certain challenges alone is part of the shamanic character and practices and has been ethnographically shown (Hayden 2003). No one is alone in this world, for we have developed as a social community of organisms, and the thing that social organisms are specialized at is working together. An assistant and others can be enlisted by the shaman to maneuver the dangerous possession state situations that SEEs can hold (Hayden 2003:60). Often the shaman strives to be a healer and protector within his or her community. This is why shamans are known to practice both healing and destructive perspectives.

During healing sessions involving shamans, the use of induced ASC can range from scenarios where the shaman is alone or involve the whole group present and the universal presence of SEEs during shamanistic healing ceremonies reflects that there is a biological and cognitive basis (Winkleman 1991, Dobkin de Rios 1983, Móró 2010). The similarity that shamanistic techniques have with therapeutic situations is that the workings of information content processing mechanisms and the subjective experience of set and setting have a measureable impact upon the physical and mental functioning of patients (Móró 2010, Schmid et al. 2010). The therapeutic commonalties between traditional SEE healing ceremonies and evidence for the therapeutic effectiveness of hallucinogens provide support for this. Winkleman (1991:15-19) and Schmid et al. (2010) clearly demonstrates this through: the findings from clinical medicine on effects of LSD; a general model of ASC, their physiological characteristics, and therapeutic effects; and laboratory studies of physiological, sensory, emotional, behavioral, and cognitive effects of hallucinogens; and the categorization of the differences in types of psychedelic users.

3. Arguments For.
The use of psychopharmacological substances, ritualistic practices, and cognitive training teaches the shaman the ability to voluntary overcome, control, and regulate SEEs. A wide range of techniques are described in traditional shamans’ repertoire and incorporate different ASC induction agents and psychobiological procedures. Winkleman (1991:17) compiled a comprehensive techniques list that includes: hallucinogens, opiates, and other drugs; extensive running or other motor behavior; hunger, thirst, and sleep loss; auditory stimulation and other forms of intense sensory stimulation such as physical torture or temperature extremes; sensory deprivation, sleep states and meditation; and a variety of psychophysiological imbalances or sensitivities resulting from hereditarily transmitted nervous system liabilities, epileptic-like states resulting from injury, disease, or other trauma to the central nervous system like extreme temperatures, or other sensitive conditions of the temporal lobe and the associated structures of the parasympathetic system. All of these techniques appear not only in the clinical literature, but also in our everyday life. It is hard not to read a story, watch a film or TV series without seeing one or another of these techniques being experience by a character and have a deep impact upon their consciousness. To me this is clearly showing how SEE occur throughout everyone’s life. Therefore it is because of this that these techniques support how SEEs have a systematic correspondence with the phenomenal experiences during contemporary pharmacologically induced ASCs practices (Móró 2010, Suefeld & Borrie, 1999). SEE induction techniques work in coaction with the manipulation of ASC by utilizing the concepts of set and setting. Set involves the individual characteristics and expectations while setting contributes through the physical and social context of the practice (Winkleman 1991, Dobkin de Rios 1984, Móró 2010).

SEEs traditionally have utilized techniques that focus on the psychobiological and emotional aspects of ASC that involve transcendence, mystical, spiritual, and transpersonal experiences and are reflected in the extensive role of the shamanistic healer in manipulating the individual’s tribal cosmology during treatment (Winkleman 1991). This was built upon techniques and elements learned during a shaman’s training and their initiations on the proper use of costumes, archetypal props, well-practiced chants, song and dance, small social nuances, and the preparation of psychoactive plants commonly seen in shamanic practice (Hayden 2003. Schmid et al. 2010).
Ethnographically, these techniques have been demonstrated in shamanic recruitment rituals as they allowed the shamanic societies of prehistoric cultures, and the priesthoods of early religion, to identify individuals who would perform well under ASC develop the ability to properly control a balance between the sacred forces (Suchman 1989, Hayden 2003). Elements of recruitment rituals and control over ASC persist today in certain subcultures that demonstrate a common positive view towards successful individuals with the SEE characteristics of ineffability, enlightenment, fleeting duration of harsh experiences, passivity of egocentric guidance, and transcendence with higher forces (Hayden 2003, Suchman 1989). Such subcultures are the fashion world, standup comedy, off-the-grid and gang communities, creative and artistic publication of alternative media, and the tattoo and body modification industries.

In all of these subcultures, sans the tattoo and body modification industry, there is an underlying concept that to be successful one must put in their time and work through a long and arduous apprenticeship that involves; the severe poverty-like living conditions, a constant state of disapproval and rejection, adopting an ideology such as “only the tough, smart, and odd survive”, and the wide use of pharmacological substances within each culture. Without having these recruitment rituals, the individual would lack the knowledge and skills to exert mental and physical control over the main cognitive and emotional factors involved in such social and businesses landscapes; repeated rejection, drastically harsh styles of criticism, extremely fast and constantly reactive lifestyles, egocentric personalities but with an ability to shift to other perspectives freely in order to gain knowledge and advantages over others situations. Recruitment rituals that involve life experience appear then too be used traditionally and contemporarily for the behavioral effects that are gained during training in ASC induction practices and manipulation.
.jpg)
Initiation and recruitment rituals can also be induced using the more structured and dogmatic techniques similar to those used today by worldwide military personal training by the application of hazing ceremonies towards new recruits. The modern day military industrial complex has bureaucratized and created tightly controlled evaluation criteria for every occupational position in their social organizational structure. This is achieved through any and all available methods of measurement and categorization of an individual and the application of that individual’s assessment models to find the most profitable and achievable mode of training. A detailed comparison is beyond the scope of this paper but supports the claim that many organizations and groups incorporate the SEEs in a variety of forms towards eliciting their desired behavioral effects.
The resulting behavioral effects that are elicited during such aforementioned SEE techniques are: a replacement of an externally orientated perspective of sympathetic dominance of cognitive processes and desynchronized activity of the frontal cortex; cessation of external behavior and focus on internally generated perspectives during high does or severe conditions; increased tendency toward exploratory behavior and arousal response reconditioning; depatterning influence on habitual experiences and a reduction in egocentric fixation; dealing with a variety of stress related perspectives such as fears, phobias, and stress and tension management; as well as personal integration, self-control and a range of physical changes. All of these behavioral changes have been clinically shown to have significant therapeutic effects when targeted at various structures of the body, brain, or mind, such as sensory modalities, movements and postures, breathing, brain metabolism, neurotransmitter levels, linguistic, cognitive, and emotional processing (Winkleman 1991, Móró 2010, Schmid et al. 2010, Hayden 2003, Suefeld & Borrie, 1999).

It is these therapeutic effects that shall now be examined in detail on the array of commonalities that current clinical and (self-) treatments share with traditional healing ceremonies shown ethnographically to be used by shamans’ (Hayden 2003, Winkleman 1991, Krippner 1991, Dokin de Rios 1977, Schmid et al. 2010, Rock et al. 2008). Móró (2010) shows us that ASC induction methods can result in an obvious causal resulting state, however this perspective has been modified and personalized in every realm that shamanic elements are present and can be separated into five categories: spontaneously occurring, physically and physiologically induced, psychologically induced, disease induced, and pharmacologically induced phenomena (Móró 2010). Due to cultural transmission different induction techniques have been combined across large timelines and social arenas. During traditional healing ceremonies and contemporary clinical research the SEE is put through a constant barrage and experimentation which has resulted in manipulating ASC for the neurological, cognitive, emotional, psychophysical, and behavioral effects that can serve as a therapeutic tool.

One case example is an analysis of Ayahuasca as a method of (Self-) Treatment by Schmid et al. (2010:188-204). Ayahuasca, botanically and pharmacologically; is made of a vine (Banisteriopsis caapi), a MAO (monoamino-oxidase) inhibitor, and usually a DMT (Dimethyltryptamine)-containing plant (Psychotria viridis or Diplopterys caberena), it’s active ingredients are the reversible MAO-inhibitor harmine and the serotonin-reuptake inhibitor tetrahydroharmine, which together make the serotonin-receptor (5-HT2) agonist component N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) bioavailable for oral use, and is relatively potent and long-acting when compared to the practice of inhalation of synthesized DMT (Schmid et al. 2010). The fully processed ayahuasca becomes an ingestible beverage that is used in the ritualistic setting of Santo Daime rituals, neo-shamanic rituals, and do-it-yourself (Self-) treatments which are commonly referred to as “healing ceremonies” (Schmid et al. 2010).
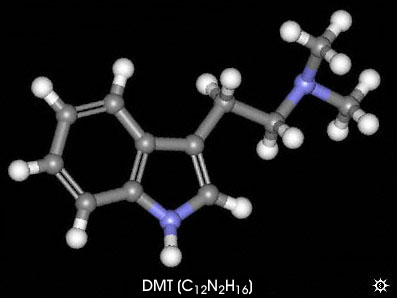
It was found that those patients who had sought (self-) treatment of their clinical conditions are that there search was guided by a common lack of confidence in the conventional medical regimes that are applied in hospitals and treatment centers. Instead, coupled with a perspective of rejection towards the “harm and addiction” propaganda surround psychoactive substances, the patients wanted a more “holistic” or “spiritual” therapy method (Schmid et al. 2010). These examples show how such patients display features of a SEE through the presence of cultural values that predispose the person toward sacred ecstatic experiences and when individuals are motivated to have such experiences and have made appropriate ritual, mental, and physical preparations for them (Hayden 2003, Schmid et al. 2010).
With this perspective in hand (Self-) treatment patients were open to actively learn to apply the appropriate training in order to elicit, what Winkleman (2005) has termed, “unspecific changes” within their therapeutic techniques. Schmid et al. (2010:197) have categorized these unspecific improvements to include nine categories: (1) A change in health behaviors including diet. Participants also often gave up alcohol or cigarettes, (2) Enhanced clarity, recognition, and sensibility, (3) Increased physical well-being, (4) Energy, power, and strength, (5) Better coping with problems and ‘‘daily hassles,’’ (6) Confidence and tranquility, (7) A renewed sense of happiness, love, and joy, (8) A change of life orientation sometimes including a strive for non-materialistic values, (9) Improved social competences. All of these unspecific changes are beneficial characteristics within clinical therapeutic strategies and share their origins with shamanic healing ceremonies.

Another therapeutic technique that has been examined clinically for its ASC manipulation potential and resulting unspecific improvements is Restricted Environmental Stimulation Therapy (REST) (Norlander et al. 1999, Suefeld & Borrie 1999). The first technique of REST is called chamber REST. The procedure follows that a subject lies down in a bed for 24 hours in a dark, sound-reduced room. Instructions are given to reduce movement but no physical restraints are used. The standard biological amenities are provided (food, water and toilets) within the room and an intercom is used so that subjects can talk to the research assistants at anytime. Across studies fewer than 10% of subjects leave the study (Suefeld & Borrie, 1999).
The second method used in REST is tank flotation. Floatation REST involves a quiet room that contains an insulated tank (of varying sizes) that contains 20-30 cm of a medium that is a skin-temperature solution (35.5 Celsius) of water and Epsom salts. This mediums density has a specific gravity of 1.15 relative to distilled water which allows for no effort to be made to float and major effort to attempt to turn over. As a result of this, a subject can relax with no concern for their safety. Similar to chamber REST, an intercom is present and communication with a research assistant is available. Tank floatation has experimental benefit that sessions on average only last 45-60 minutes compared to chamber REST sessions of 24 hours.

Chamber and Floatation REST methods are similar to the sensory overstimulation and deprivation practices used traditionally by shamans and religious practioners. This is ethnographically shown by such techniques of the St. Lawrence Island Eskimos where shamanic training involves a 5-day episode where they "go out of their minds," staying outside during snowstorms without eating or drinking, enacting death and resurrection rituals, and displaying strength so unusual that "ten men cannot hold them" (Suchman 1989). Similar psychological Effects of REST can be seen in clinical multitreatment stress management therapies.
A common treatment technique used in hospitals is Relief from Stimulus Overload in order to reduce patients suffering from drug-induced mania. It is also used by neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) in the treatment of premature infants and infants born addicted to heroin, cocaine or alcohol (Suefeld & Borrie, 1999). In retirement and pediatric care units REST techniques have been shows to statistically improve mental and emotional characteristics, reduce weight gain, help quit smoking, and lowered levels of agitation (Suefeld & Borrie, 1999). Chamber REST has also been used in conjunction with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) to lower the rates of subjective memory loss brought on by ECT (Suefeld & Borrie, 1999). It is proposed that due to the aforementioned therapeutic findings and their commonalities with the prehistoric shamanic elements and techniques, it can be clearly shown that within Western culture these traditional shamanic rituals have taken on a more contemporized view of inducing a therapeutically beneficial SEE.
As a final line of evidence for shamanic elements playing a role in western culture the interrelationship of shamanic manipulation and control of magic to today’s issues of intellectual property rights shall be examined. This concept was proposed and discussed by Suchman (1989) due to his analysis that magic and intellectual property rights both involve control over abstract and linguistic perspectives and figure prominently in numerous aspects of daily life. Using the economics of intellectual property, the anthropology of law, and the ethnography of magic Suchman (1989) reaches some rather interesting conclusions.

One is how magic was intimately intertwined within preliterate society’s most sophisticated technologies and the practical components of their techniques (Suchman 1989). Because of this, magical services gained the ability to be sold or traded within the community for either tangible or intangible remuneration. By applying such social magic systems, the shaman or priesthoods dictate the conditions of access to proprietary nonintellectual commodities (such as magical talismans, rituals, psychoactive plants, and ceremonies) on the purchase of technological services that they could not otherwise monopolize, which today is reflected in what patent holders refer to as a tying agreement (Suchman 1989). Magical services also enroll strength from elaborate cultural constructs of a “mythology of risk” that controls for external threats in the same way that litigation threats chill infringement of Western intellectual property rights (Suchman 1989).

What Suchman’s (1989) perspective brings to the table is that economic theorists can gain new insights into their models through the understanding of such prehistoric methods of magic and religious information systems. Extensive innovation imposes high information costs, extensive record keeping, and flourishing economies which characterizes contemporary industrial society, but most likely may not have had much application within prehistoric communities (Suchman 1989). Prehistoric communities on the other hand cannot withstand the pressures of constantly embracing new technologies due to disruptions in the social order and established methods of production (Suchman 1989).
Yet, it is important to note that the shamanic elements of recruitment rituals and training methods restrict creativity activity and ASC experimentation to a relatively small and isolated subgroup, buffing society’s core cognitive technologies and therapies from unproven techniques (Suchman 1989). It is these exact features that are essential to the academic and scientific research methodologies. The scientific method has often been compared with the old practice of alchemy, but it also appears to share shamanic elements with the management of intellectual property and the importance of peer-reviewed publications.
4. Arguments Contra.
The most common argument against the presence of shamanic elements and their techniques being present within Western culture is that of language. The terminology issues within academia are consistently present due to the fact that each article and discussion of abstract concepts must be operationally and experimentally defined. The variables need to be set in stone.
This though is hard to achieve both during scientific discussions, as well as layman discussions, about ASC involve subjective experiences and the adjectives used to describe them. This issue can be dealt with by incorporating definitions that are based on statistical notions instead of solely the perceptually and culturally biased notions (Móró 2010). The PCI mentioned above is a clear rendition of attempts to solve this problem (Pekala et al. 1991).

It has been suggested that the therapeutic effects of SEE are nothing but a placebo effect due to set and setting and that “The hallucinogen does not in itself effect a cure but rather plays the role of a medicinal aid to be used in the total context of psychoanalysis and psychotherapy” (Schultes and Hoffmann 1979:178). The overwhelming clinical evidence indicates that hallucinogens change experience and awareness and by inducing measureable unspecifc improvements showing support against the placebo argument and has been examined previously in this paper (Pekala et al. 1991, Winkelman 1991).
5. Alternative Explanations.
It appears that the most common alternative explanation for shamanic elements and their techniques are related to the parapsychological concept of Psi. It is a term that collectively refers to reported interactions and anomalies of behavior between organisms and their environment in which information or influence has taken place that cannot be explained using current scientific measures of physical properties (Krippner 1991). Many of these reported interactions come from ethnographically and contemporary accounts of events featuring elements of shamanic practices. William James’ (1982) crucial work on the topic, The Varieties of Religious Experience, has been cited thoroughly in parapsychological literature and as well, within theological and anthropological discussions concerning religious techniques.
Essential to the parapsychological perspective of shamanic elements and techniques is the assumption that the phenomena under investigation are lawful, natural, and which can at some point be explained by the scientific discovery and revision of the current scientific worldview. A key alternative route of investigation of the psi properties of shamanic practices would be to examine a controversial revision of the scientific worldview proposed by Dean Radin (1997).

Radin’s (1997) revision involves current science to come to the realization that the ancient concepts of sacred forces and magical talents may be explained through the theory of a conscious universe. Radin (1997) states that the theories of quantum mechanics and specifically non-locality theory support the notion that psi phenomena are physically possible due to the capacity of the conscious mind to connect with and manipulate the chaos of quantum mechanics in order to impose a conscious will upon the physical world, be this through the technique of telepathy, remote viewing, clairvoyance, precognition, or psychokinesis. If such a claim is accurate then further research and discussion shall be needed on the explanation and effects that are produced during ASC and SEEs.
6. Conclusions.
The aim of this paper was to inspect the persistence of shamanic elements and their techniques within Western culture through the use of psychopharmacological substances, ritualistic practices, and cognitive training. It has been shown that the appropriate training techniques for inducing an ASC work in coaction towards attaining a SEE within various contemporary society settings. Shamanic elements of healing and their therapeutic applications were examined in order to demonstrate that their traditional uses have developed and emerged as brand new aspects of psychedelic, medical, and therapeutic culture. The investigation of topics such as magic and intellectual property rights was able to illustrate that current knowledge can benefit from an understanding of shamanic social techniques and the symbolic power behind language and ideologies.
This symbolic power of language though is the essential feature of the arguments against the ideas postulated in this paper. Terminology clearly must be dealt with in any attempt at future research related to the formation and occurrence of SEE within current scientific models. The parapsychological worldview as an alternative explanation may cause further disturbances in the debate of terminology over the physical and statistical notions of the vary properties of the universe.
7. References
Aghajanian, G.K., and Marek, G.J.
1999 Serotonin and hallucinogens. Neuropsychopharmacology 21(25):16S-23S.
Dobkin de Rios, Marlene.
1984 Hallucinogens: Cross-Cultural Perspectives. University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque.
Dobkin de Rios, Marlene and Balaji Munkur.
1977 On the Serpent Cult and Psychoactive Plants. Current Anthropology 18(3):556-558.
Hayden, Brian.
2003 A Prehistory of Religion: Shamans, Sorcerers, and Saints. Smithsonion Books, Washington.
James, William.
1982 The Varieties of Religious Experience. Viking Penguin Inc, London.
Krippner, Stanley.
1991 Research Strategies in the Study of Shamanism and Anomalous Experience. The Anthropology of Consciousness 2(1-2):13-19.
Meyer, J. S., and L. F. Quenzer.
2005 Psychopharmacology: Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, Massachusetts.
Móró, Levente.
2010 Hallucinatory altered states of consciousness. Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences 9:241-252.
Norlander, Torsten, Henrick Bergman, and Trevor Archer.
1999 Primary process in competitive archery performance: Effects of floatation REST. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology 11(2):194-209.
Pekala, R. J., J. Steinberg, and V.K. Kumar.
1986 Measurement of phenomenological experience: phenomenology of consciousness inventory. Perceptual and Motor Skills 63(2):983-989.
Radin, Dean.
1997 The Conscious Universe: the scientific truth of psychic phenomena. HarperEdge, San Francisco.
Rock, Adam J., Jessica M. Wilson, Luke J. Johnston, and Janelle V. Levesque.
2008 Ego Boundaries, Shamanic-Like Techniques, and Subjective Experience: An Experimental Study. Anthropology of Consciousness 19(1):60-83.
Schmid, Janine Tatjana, Henrik Jungaberle, and Rolf Verres.
2010 Subjective Theories about (Self-) Treatment with Ayahuasca. Anthropology of Consiousness 21(2):188-204.
Schultes, Richard Evans, and Albert Hoffman
1979 The Plants of the Gods. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Suedfeld, Peter, and Bow, Roderick A.
1999 Health and therapeutic applications of chamber and flotation restricted environmental stimulation therapy (REST). Psychology & Health 14(3):545-566.
Suchman, Mark C.
1989 Invention and Ritual: Notes on the Interrelation of Magic and Intellectual Property in Preliterate Societies. Columbia Law Review 89(6):1264-1294.
Winkelman, Michael.
1991 Therapeutic Effects of Hallucinogens. The Anthropology of Consciousness 2(3-4):15-19.
 Does it really need to be reexamined? Well of course it does. A clear example of this can be seen in the widely used definitions stating what ASC exactly are (Aghajanian & Marek, 1999; Dobkin de Rios, 1984; Dobkin de Rios & Munkur, 1977; Meyer & Quenzer, 2005; Móró, 2010; Randolph-Seng, 2009; Schmid et., 2010; Winkelman, 1991). I feel that Móró's (2010) working definition collects together the most important features through the use of self-mapping procedure which concludes; "A hallucinatory altered state of consciousness is a transiently stable mode of operation of supervenient levels in the mind-brain complex, where objectively detectable characteristic changes in the internal information processing mechanisms of neurocognitive subsystems may be subjectively experienced as changes in phenomenal content and overall psychological functioning, as compared with prior and posterior baseline states of the individual."
Does it really need to be reexamined? Well of course it does. A clear example of this can be seen in the widely used definitions stating what ASC exactly are (Aghajanian & Marek, 1999; Dobkin de Rios, 1984; Dobkin de Rios & Munkur, 1977; Meyer & Quenzer, 2005; Móró, 2010; Randolph-Seng, 2009; Schmid et., 2010; Winkelman, 1991). I feel that Móró's (2010) working definition collects together the most important features through the use of self-mapping procedure which concludes; "A hallucinatory altered state of consciousness is a transiently stable mode of operation of supervenient levels in the mind-brain complex, where objectively detectable characteristic changes in the internal information processing mechanisms of neurocognitive subsystems may be subjectively experienced as changes in phenomenal content and overall psychological functioning, as compared with prior and posterior baseline states of the individual." Alterations of ASC have been a feature of ritualistic shamanism for generations, and over these generations the induction techniques have found that during transitions between one state to another, a sort of inertia can occur. This inertia overlaps the past mental states with the current one and even the future mental states reverberate back depending on the induction method used. Through training, individuals create automatic physical, cognitive, and behavioral reflexes, reactions, and associations in order to gain mastery over their internal mental states during ASCs and SEEs and return to their present perspective (Hayden, 2003; Winkelman, 1991; Krippner 1991).
Alterations of ASC have been a feature of ritualistic shamanism for generations, and over these generations the induction techniques have found that during transitions between one state to another, a sort of inertia can occur. This inertia overlaps the past mental states with the current one and even the future mental states reverberate back depending on the induction method used. Through training, individuals create automatic physical, cognitive, and behavioral reflexes, reactions, and associations in order to gain mastery over their internal mental states during ASCs and SEEs and return to their present perspective (Hayden, 2003; Winkelman, 1991; Krippner 1991).  It is these features of REST that I have proposed should be incorporated into the examination of the theoretical cognitive and neurological models of ASC and SEEs. One model that has briefly been examined using REST is that of implicit and explicit learning models of procedural memory (Norlander et al., 1999). The researchers applied REST to inspect how REST can be applied to reinforce the primary process orientation to enhance the quality of coaching and training methods that occur in individualized sports, such as competitive archery (Norlander et al., 1999).
It is these features of REST that I have proposed should be incorporated into the examination of the theoretical cognitive and neurological models of ASC and SEEs. One model that has briefly been examined using REST is that of implicit and explicit learning models of procedural memory (Norlander et al., 1999). The researchers applied REST to inspect how REST can be applied to reinforce the primary process orientation to enhance the quality of coaching and training methods that occur in individualized sports, such as competitive archery (Norlander et al., 1999).





























.jpg)











